Natural Garlic Oil FCC Grade is extracted from the fresh garlic seed by steam distillation method. It is 100% pure natural oil for the food seasoning, healthcare supplement, etc.
Why is garlic a great health herb?
It has the vital chemical compound Allicin that is the wonder therapeutic ingredient for its qualities. The allicin compound contains sulfur, which gives the garlic its pungent savor and peculiar smell. The health benefits of garlic are innumerable.
Garlic is the oldest known healthcare plant variety or spice in existence. Mankind recognized the curative qualities of this magic herb since over 3000 years. Sir Louis Pasteur, the discoverer of penicillin effectively utilized the anti-bacterial qualities of garlic way back in 1858.
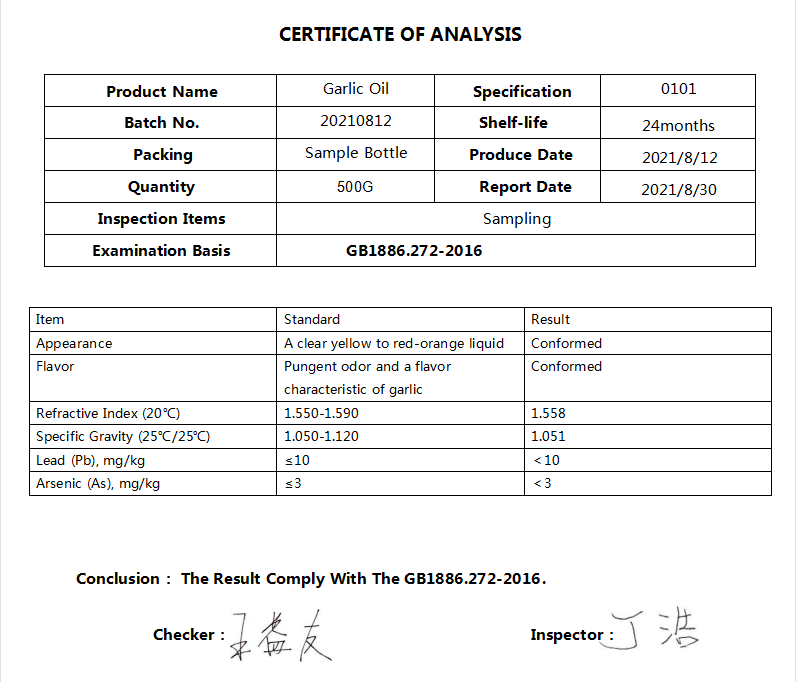
Product Name
|
|
Latin Name
|
Allium sativum L.
|
Part Used
|
Garlic Bulb
|
Specification
|
100% Natural (C14 Test) FCC Grade
|
Color
|
Clear Yellow to Red-orange
|
Appearance
|
Oil Liquid
|
Active Ingredient
|
Allicin, Thioether Compound
|
Flavor
|
Pungent odor and a flavor characteristic of garlic
|
Refractive Index (20℃)
|
1.550~1.580
|
Specific Gravity(20℃)
|
1.050~1.095
|
Diallyl disulfide(%)
|
≥25
|
Diallyl trisulfide(%)
|
≥25
|
Package
|
25KG/50KG Steel-HDPE Bucket
|